TSMC crushes Samsung in Q2 chip production as more 5G demand beckons

When it comes to firms that manufacture chips for customers, the company that you probably think of first is TSMC. After all, the Taiwan based firm is the largest contract foundry in the world and produces chips for companies like Apple, Huawei (at least for the moment), Qualcomm, MediaTek, and others. The second-largest independent foundry is owned by Samsung and both are the only chip manufacturers in the world that will produce chips this year using the more powerful and energy-efficient 5nm process node.
Samsung's 18.8% second-quarter global foundry market share is swamped by TSMC's 51%
According to the Nikkei Asian Review, Samsung is opening its vault and spending some money to take on TSMC in the arena for 5G chips. The next generation of wireless connectivity, 5G will eventually deliver download data speeds for consumers 10 times faster than 4G LTE. It will lead to the creation of new technologies and industries. Despite a challenge from Samsung, the Nikkei Asian Review notes that TSMC's lead in the production of 5G chips might be insurmountable.
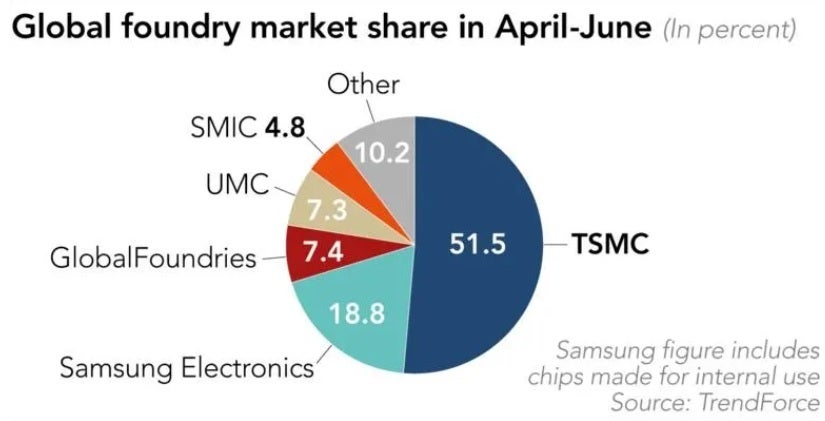
TSMC owned 51% of the global foundry market during the second quarter
Even when the COVID-19 pandemic might have presented a challenge to TSMC, an executive of a Japanese company that is a supplier to the foundry said that, "demand from TSMC has not flagged and more staff are needed." The $40 billion Tainan factory that TSMC broke ground on in 2018 is churning out 5nm Apple A14 Bionic chipsets that are designed by Apple, but are produced in Taiwan. If all goes as intended, the 5G 2020 iPhone 12 family will be the first smartphones in the world to be powered by a 5nm chipset. The new process node will allow each chip to contain a mind blowing 15 billion transistors. Compare that to the current 7nm A13 Bionic chips produced by TSMC that will feature 8.5 billion transistors inside. The more transistors inside a chip, the more powerful and energy efficient it is.
TSMC is also producing 5nm chips for Huawei's HiSilicon semiconductor unit. However, the largest phone manufacturer in the world at this moment, Huawei has quite a pickle to figure out. Because the U.S. government considers the company to have very close ties to the communist Chinese government, it is concerned that the Chinese manufacturer spies on Beijing's behalf. As a result, a new export rule put into place in the middle of May prevents foundries around the world from shipping chips to Huawei if they are made using U.S. origin technology. The U.S. is allowing TSMC to produce 5nm chips from wafers that were already in production as long as the shipments are made no later than 120 days from May 15th (September 12th).
Despite contributing 15% of TSMC's revenue last year, Huawei's impending removal from TSMC's customer roster hasn't forced the foundry to make any changes when it comes to spending. Last month at the company's stockholder meeting, Chairman Mark Liu said there would be no change to the $15 billion to $16 billion in capital spending plan for the year ending December 2020. The company can handle such problems because of the way it handles its cash flow. One financial industry insider calls a chart of TSMC's cash flow "a work of art. It's completely different from the uneven graphs of Japanese electric machinery makers." The insider says, "Painting a textbook-like cash flow graph is rare in the semiconductor industry, which is prone to fluctuations."
Even though Huawei will leave big shoes to fill at TSMC where it is the second largest customer after Apple, it's full speed ahead for TSMC in Tainan where 3nm chips could roll out as soon as 2022 thus keeping the observation made by Intel co-founder Gordon Moore alive for the moment. In the mid 1960s, Moore's Law called for the transistor density in integrated circuits to double every year. Eventually, this was changed to every other year and while it hasn't been perfect, check out the most recent progressions: 7nm chips like the A13 Bionic and the Snapdragon 865 Mobile Platform shoehorn approximately 96.5 million transistors into each square mm. The 5nm semiconductors due out during the second half of the year will squeeze 171.3 million transistors into each square mm, and the 3nm process node will pack 300 million transistors into each square mm.
During the second quarter of this year, TSMC had 51% of the global foundry market. Samsung, including chips made for its own products, was next with 18.8%. Global Foundries owned a 7.4% slice of the global foundry pie from April through June and UMC was next with a 7.3% share. SMIC, China's largest foundry, captured 4.8% of the market during the second quarter.










Things that are NOT allowed: