Apple Pay explained - technology, security, and payment methods

NFC (near-field communication) is a set of short-range wireless technologies that connect devices at a distance of up to 10cm through a radio frequency field. NFC-connected devices can take very simple and small form factors, such as tags, stickers, key fobs, or cards. James Andreson, MasterCard's senior VP of mobile and emerging payments, expects NFC to become "the predominant technology for point-of-sale payments" between a smart device and merchant terminal. Perhaps Apple Pay could be the push his prediction needs to be fulfilled.

The element has its own embedded operating system, power supply (a small battery) and its own processors and RAM memory. All data storage areas, which is where your credit card and fingerprint information will reside, are protected against both physical and software attacks, and the flow of data goes through a number of interfaces and micro-controllers, protected by various types of end-to-end encryption (Public Key Infrastructure, Dual / Triple key DES-3). Apple Pay takes your banking information and generates an unique Device Account Number, which is encrypted and stored inside the Secure Element. The chip is included in both the iPhone and the Apple Watch.
Touch ID, found on the iPhone 5s and iPhone 6, is built inside the smartphone's home button. It is protected with a laser-cut sapphire crystal so as not to scratch, which would prevent it from operating properly. It also features a stainless steel detection ring to detect the user's finger. Fingerprint data is stored in a secure enclave inside the iPhone's processor, most likely the Secure Element we spoke of above. Fingerprint reading isn't used for payments with the Apple Watch - instead, you are expected to double-press the button below the Digital Crown. As the Watch is pretty tightly strapped on your wrist and in no risk of being tampered with when you're on the go, putting a fingerprint sensor on it would have been over the top.
How to use Apple Pay in stores? First things first, you'll have to add your credit card information to the Passbook app. You can enter it manually or photograph your card with the iSight camera. At the moment, the system supports Visa, MasterCard, and American Express banking cards issued by American Express, Bank of America, Capital One, Chase, Citi, and Wells Fargo. Apple lists Barclaycard, Navy Federal, PNC, USAA, and US Bank as "coming soon".
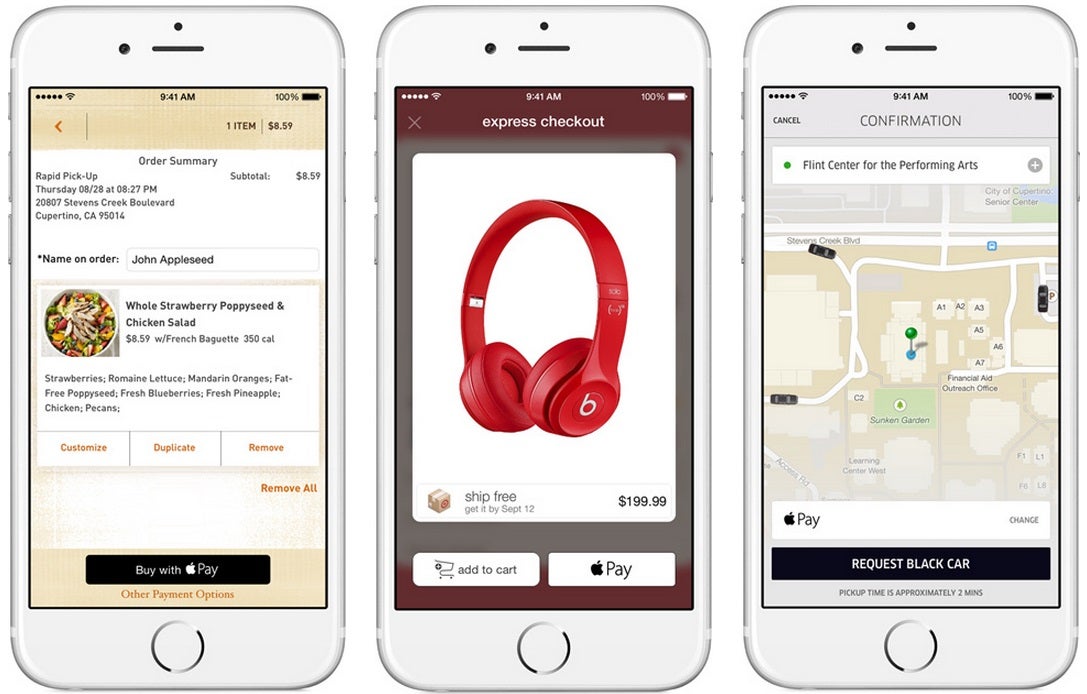
At launch, Apple Pay will be accepted at 220 000 stores and up. Users will be able to use their iPhone and Apple Watch at Babies R Us, Bloomingdales, Disney establishments, Duanereade, Macy's, McDonalds, Nike, Petco, Staples, Subway, Toys R Us, Unleashed, Walgreens, and Whole Foods Market. In addition, purchases through the following apps are supported: Groupon, Instacart, MLB.com, OpenTable, Panera Bread, Sephora, Starbucks, Target, Tickets.com, and Uber.
Shopping at a retailer and paying with Apple Pay will be something like this - the shop's register will have an NFC-enabled credit card terminal at which you hold the iPhone for a second, put your finger on the Touch ID button, and that's it - no apps and passwords. If you have the Apple Watch on you, you have to double-press the button located beneath the crown, and hold the watch to the terminal. Of course, there's no Touch ID security involved, but Apple has ensured a secure payment process by generating a dynamic, secure code for each transaction and keeping your credit card number private. The Apple Watch uses a scaled-down version of Passbook, which probably means it will let users choose which credit or debit card to use. Upon successful payment, the watch vibrates and beeps.
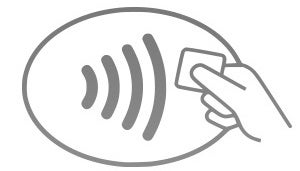
Seeing this symbol in an establishment means you'll be able to use Apple Pay.
It won't be long before Apple Pay is available to customers - it will launch next month in the USA. Now that you know what the system is all about, we can only wish you happy shopping!
Follow us on Google News












Things that are NOT allowed:
To help keep our community safe and free from spam, we apply temporary limits to newly created accounts: